Using socat to bridge interfaces
Brief
Whenever it comes to connecting two interfaces together on Linux, socat is my go-to tool. It is a flexible tool that basically create links between anything to anything.
socat establishes two bidirectional byte streams and transfers data between them. These byte streams could be constructed from a very large set of different types of sinks and sources, which makes it very powerful.
When I say anything, I really mean anything. Here are some examples of what socat can connect:
- TCP sockest
- UDP sockets
- Unix domain sockets
- IP raw sockets
- Serial ports
- Pseudo terminals
- Files
- Pipes
- Applications (EXEC)
Even very special endpoints such as SOCKS, TUN/TAP interfaces and OPENSSL are supported. No need to list them all here, the manpage [1] does a great job at that.

Just to list a few examples of how I have used socat in the very last months:
- Forward a serial port over the network
- Create virtual serial ports
- Acting as a TCP to UDP bridge
- Acting as as a TCP proxy
IOW, socat, is nothing that gets rusty in my toolbox.
How to use socat
The syntax of socat is quite simple. You just need to specify the two endpoints you want to connect, that's it.
Here are some examples:
Connect STDIN/STDOUT to a TCP socket:
1socat TCP-LISTEN:1234,reuseaddr -Forward connections from local port 8080 to another host:
1socat TCP-LISTEN:8080,reuseaddr,fork TCP:10.0.0.5:80Or act as a TCP server exposing your serial port:
1socat -v TCP-LISTEN:5000,reuseaddr /dev/ttyS0,raw,b115200Real world use case
The last example is how I used socat just the other day. I had a U-Blox GPS module connected to my embedded Linux boars via a serial port. I wanted to configure the GPS module using U-Blox's u-center software, which unfortunately only runs on Windows.
Yes, GPSD [2] has the ubxtool utility that can configure U-Blox modules and the pyubx2 library [3] is also a very nice piece of work to do this. But in this case, I also needed the configuration file created by u-center for later use.
U-center2 supports connecting to GPS modules over serial, UDP and TCP, so I basically connected the serial port on my embedded system to a TCP server:
1socat TCP-LISTEN:5000,reuseaddr /dev/ttyS0,raw,b9600Then it is just to connect to the TCP server from u-center:
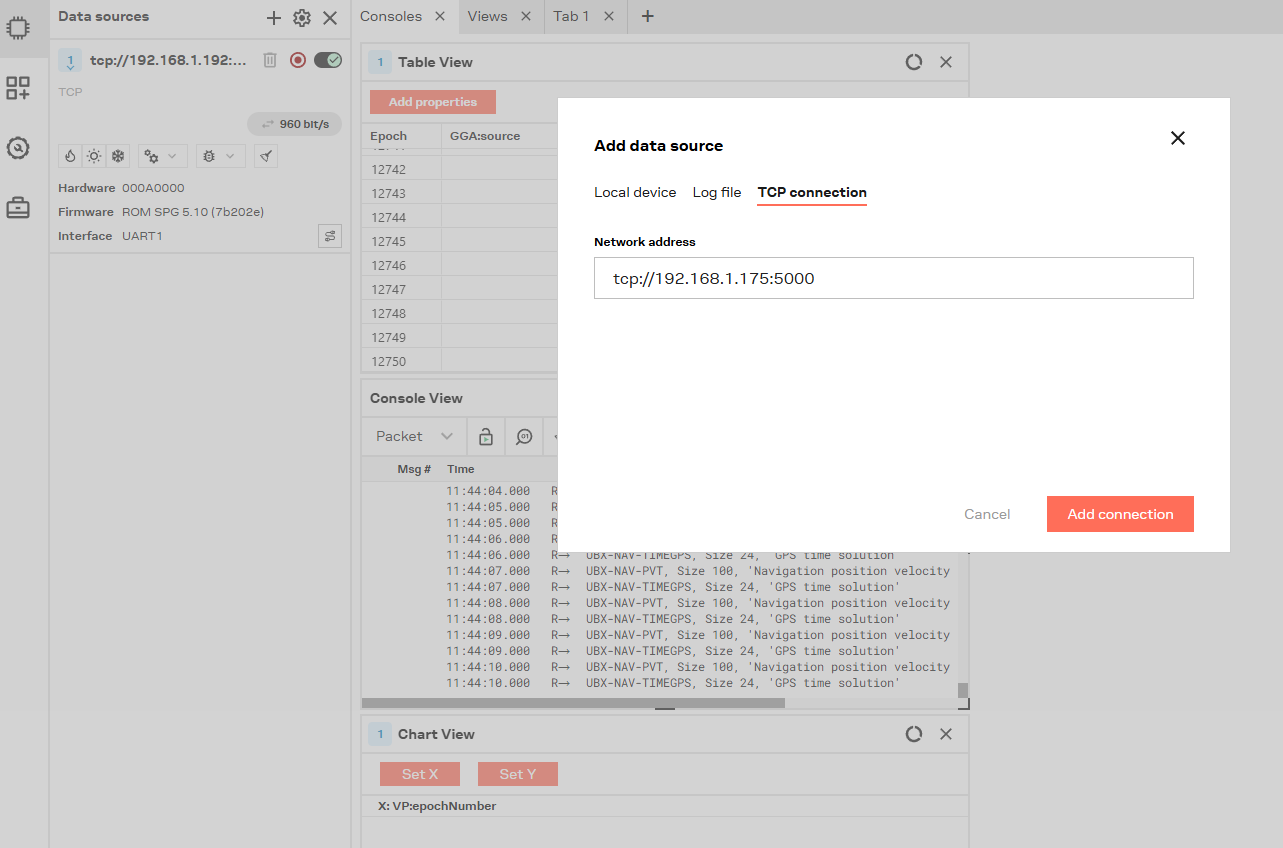
That is pretty much it.
If I wanted to use ubxtool or pyubx2, I could have used socat to create a virtual serial port on my (Linux):
1socat TCP:192.168.1.175:5000 pty,link=/tmp/ttyV0,raw,echo=0To simple bridge the serial port from my embedded system to a virtual serial port on my laptop. /tmp/ttyV0 would then behave like a local serial port, and any data sent to that port would be forwarded to the GPS module over TCP.